
Basic Layout and Working of a Thermal Power Plant
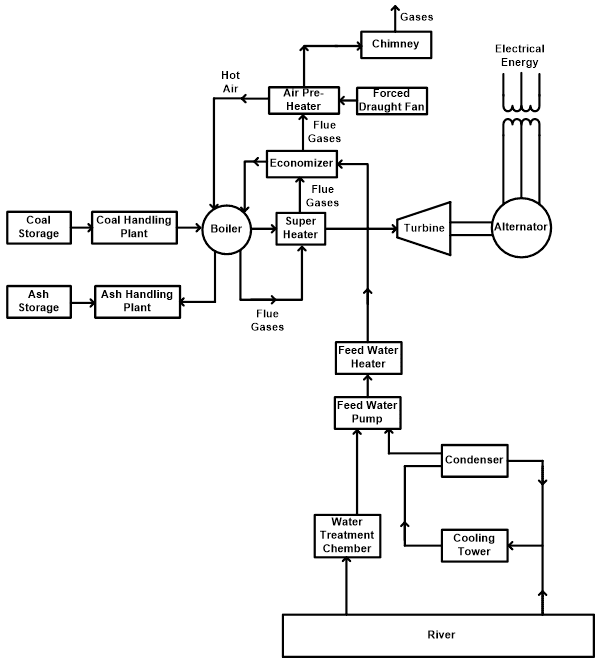
Layout of a typical thermal power plant: The thermal power station layout is given in the figure. The main components of a thermal power station are a boiler, turbine, generator and cooling tower. The function of each component is as follows: - Boiler: The purpose of the boiler is to convert water into high-pressure steam.
Thermal Power Plant Components, Working and Site Selection
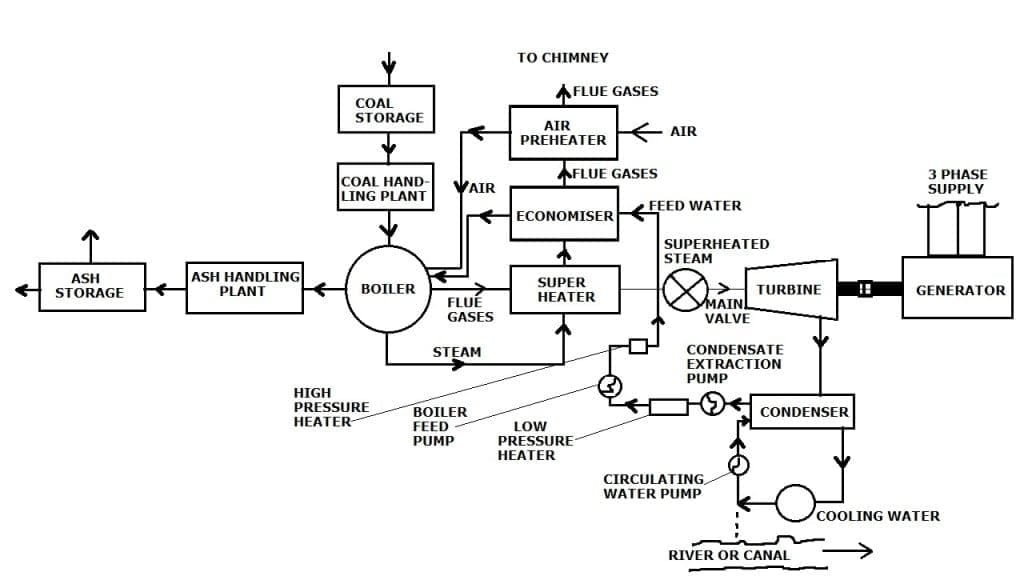
Fig. 1: Elementary block diagram of modern steam power station. Working and Construction of Thermal Power Plant It consists of the following stages: Coal and Ash Handling Arrangement: The coal and ash handling plant generally consists of: (i) Coal storage, (ii) Coal handling plant, (iii) Ash handling plant, and (iv) Ash storage.

Typical layout of CFBC based thermal power plant. Download Scientific Diagram
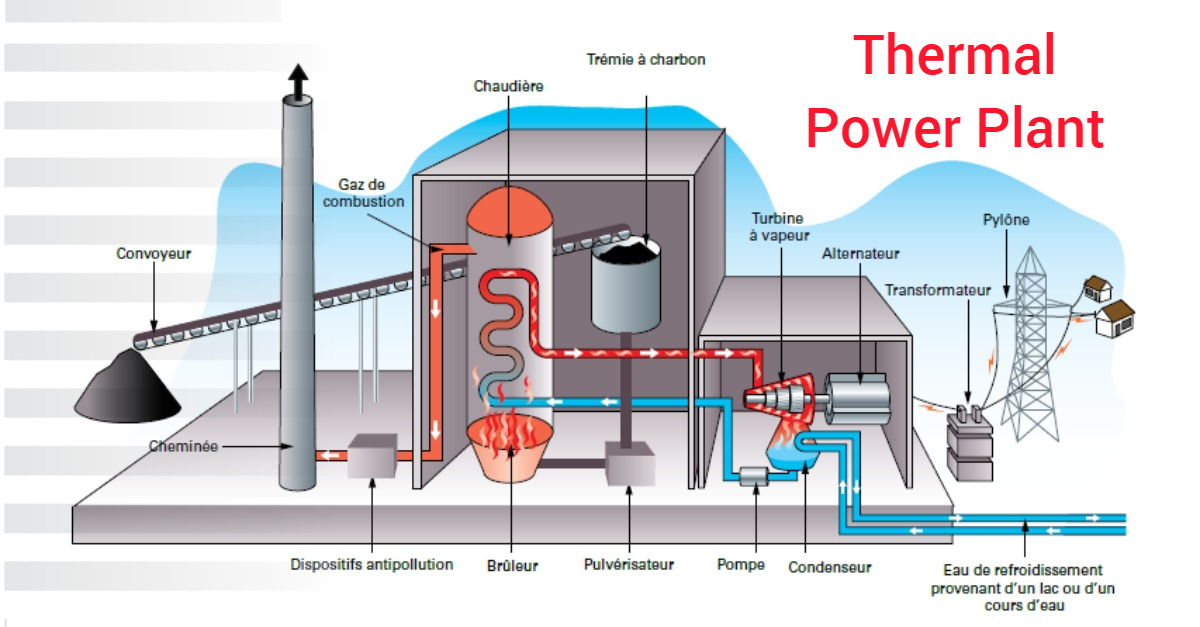
A thermal power plant, also known as a thermal power station, is used to transform heat energy into electric power for domestic and industrial applications. Electric power is generated by steam-powered turbines, which convert heat to mechanical power. So let's understand the basics of a thermal power plant.
How a Thermal Power Plant Works?
This is known as ranking cycle. This article explains how electricity is generated in thermal power plants. As majority of thermal power plants use coal as their primary fuel, this article is focused on a coal fired thermal power plant. Typical layout and working of a Thermal Power Plant

Thermal power plant
The thermal power plant, also known as a thermal power station, is used to convert heat energy into electricity for residential and commercial usage. Steam-operated turbines turn heat into mechanical power, which is then converted into electric power in the electric power production process.
Thermal Power Plant Definition, Layout, Working, Site Selection, Advantages, Disadvantages
Figure: Schematic diagram of a Thermal power plant. Selection of site for thermal power plant • Nearness to the load centre: The power plant should be as near as possible to the load centre to the centre of load .So that the transmission cost and losses are minimum. This factor is most important when Dc supply system is adopted.
Introduction to thermal power plant
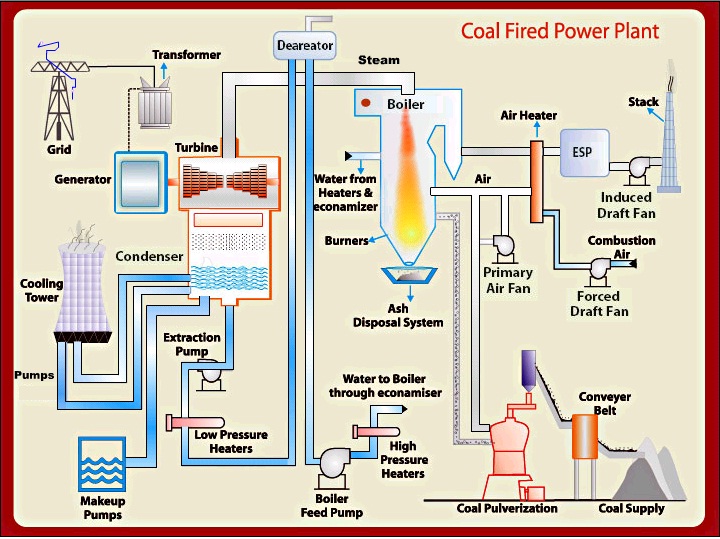
Basic Layout of Thermal Power Plant Components of Thermal Power Plant (1). Coal Storage and Pulverizer: (2). Water Boiler: (3). Steam Turbine: (4). Condenser : (4). Alternator: (6). Feed Water Pump: (7). Chimney: Working of Thermal Power Plant Advantages of Thermal Power Plant Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant Conclusion
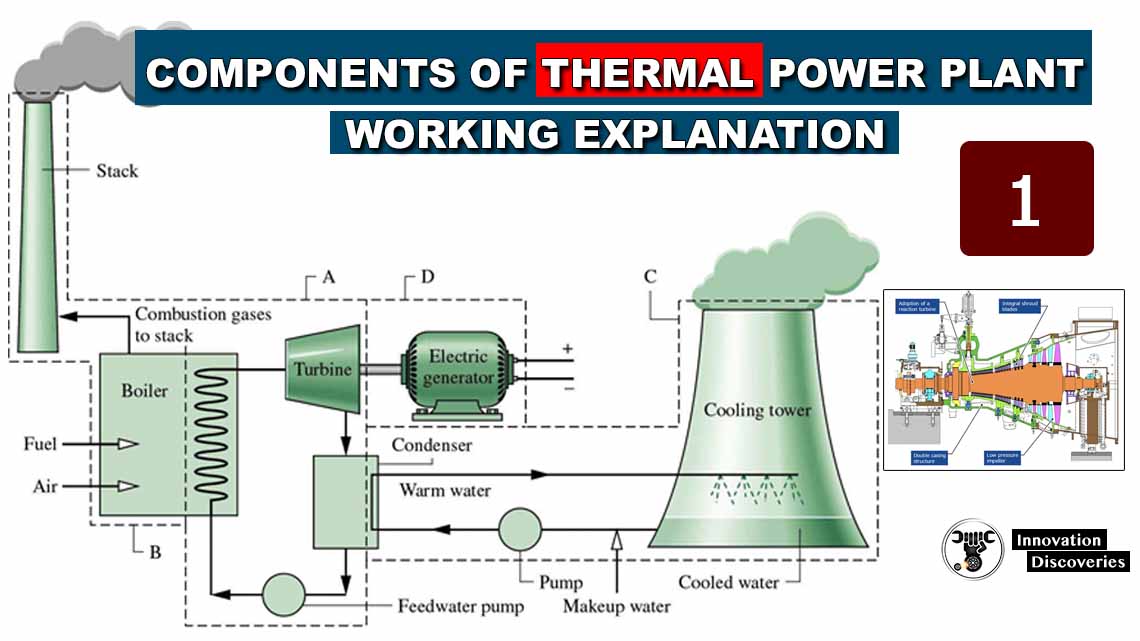
Components of Thermal Power Plant & Working Explanation
Thermal Power Plant: Design and Operation deals with various aspects of a thermal power plant, providing a new dimension to the subject, with focus on operating practices and troubleshooting, as well as technology and design. Its author has a 40-long association with thermal power plants in design as well as field engineering, sharing his.

CAD / CAM Plastic And Acrylic Thermal Power Plant Layout Model ID 25558285212
Thermal Power Plant is an electric producing power plant in which fuel (such as coal, liquefied fuel, uranium, and natural resources) is used to generate heat and that heat is further utilized to heat the water to make steam and that steam is used to rotate the turbine and further electricity generates with the help of 3 phase supply generator.
Thermal Power Plant Components & Working Principles Thermodyne Boilers
Thermal Power Plant Layout Steam power plant simply involves the conversion of heat energy into electrical energy. The method of arrangement can be divided into the following stages, Coal and ash handling arrangement Thermal power generation Generating plant Steam turbine Alternator Feed water Cooling arrangement Coal and Ash Handling Plant
.jpg)
Conventional Sources of Energy Definition, Types, Examples Teachoo
A thermal power plant is a facility that transforms thermal energy into electrical energy. Thermal energy usually comes from burning fuel, but there are also thermal power plants that can operate on geothermal and solar energy.
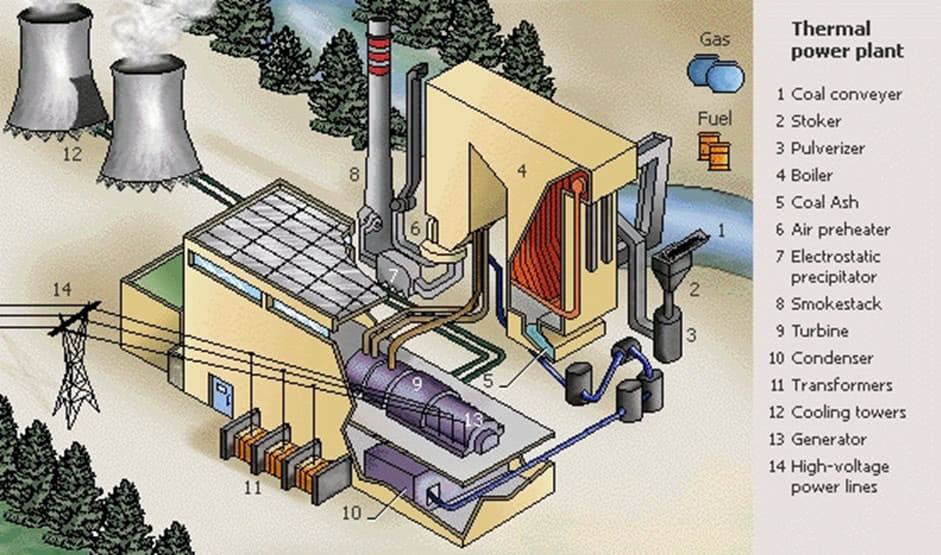
Thermal Power Plants Components & Working Principle EE Power School
Thermal power plant also called thermal power station or steam power plant is used to generate electricity. How electricity is generated in thermal power plant? In thermal power plants, the heat energy obtained from the combustion of fuel (coal/natural gas/other carbon base fuel) is used to convert water into steam.

Solar thermal power plant layout component isometr
The overall efficiency of the power plant is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent of electrical output to the heat of combustion (about 29%). The losses that occurred in the thermal power plant at various stages are as follows. Boiler House Losses: (a) To dry flue gases 5%. (b) To moisture in gases 5%.
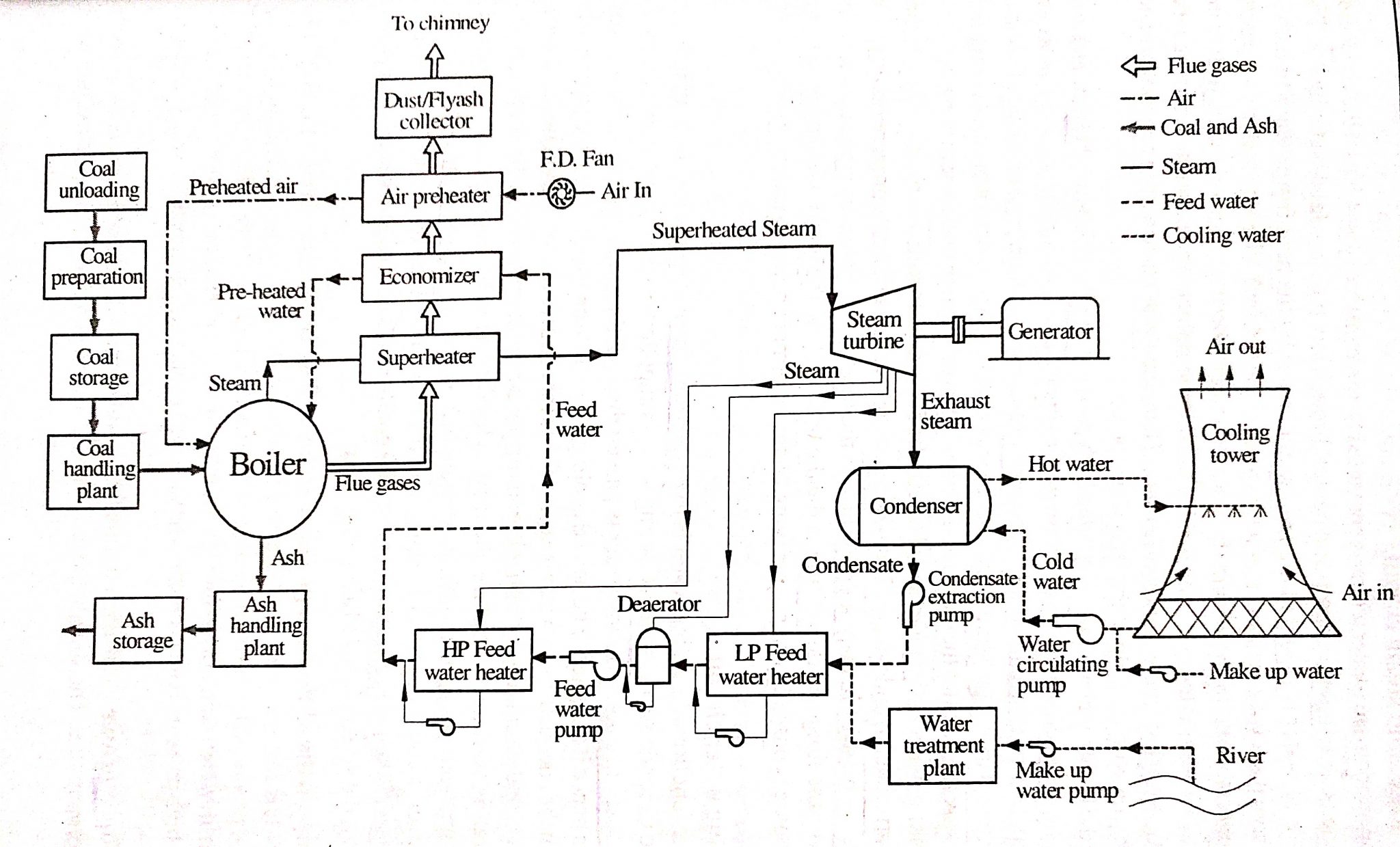
General Diagram Thermal Power Plant, Main Components Melezy
Table of Contents What is a Thermal Power Plant? Working of Thermal Power Plant Components of Thermal Power Plant Site Selection of Thermal Power Plant Efficiency of Thermal Power Plant Advantages & Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant What is a Thermal Power Plant? According to energy conservation law, energy is neither created nor destroyed.

How Thermal Power Plant Works? Layout, Working, Types & More
Fossil fuels are mainly used in thermal power plants to generate electricity, especially coal, which accounts for 76% of the electricity generated in the country.According to the ministry, coal production in 2021 will increase by 6% compared to 2020.India's total thermal power generation capacity as of January 2021 is 231,870.72 MW.. Layout of Coal-Based Power Plant:- The layout of the steam.
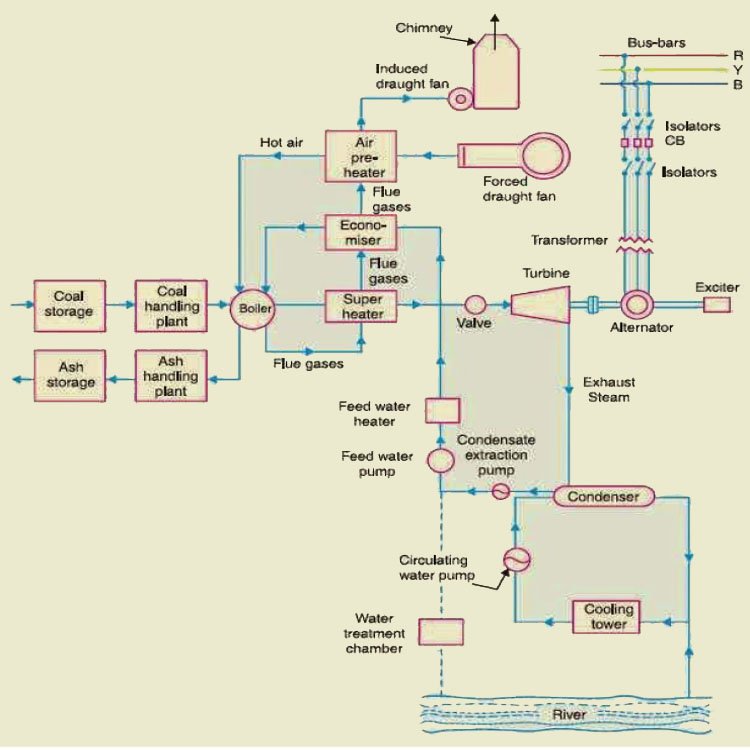
What is Thermal Power Plant? Layout, Working and Operation
A thermal power plant is a power generation station that converts the heat energy produced by the combustion of fuel into electric energy. The heat energy of the fuel is used to convert water into steam at high pressure. This high-pressure steam is passed over the turbine.